Quality Control
4 Topics
Instrumentation
DEFINITION OF TERMS:
- Energy: entity that this transmitted by electromagnetic waves
- Wavelength: defined as the distance between two successive peaks
- Nanometer: unit expression of wavelength
- Frequency: number of waves that passes a point of observation per one unit of time
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
- Measures transmitted light in a colored solution
- Measurement is based upon Beer-Lambert-Bouguer Law (Beer’s Law/Beer-Lambert’s Law)
BEER-LAMBERT LAW
- States that concentration of an unknown analyte is directly proportional to the light absorbed and inversely proportional to light transmitted.
- Absorbance is proportional to the inverse log of transmittance
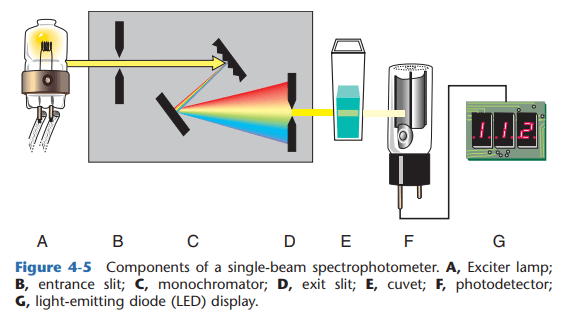
SINGLE-BEAM SPECTROPHOTOMETER
DOUBLE-BEAM SPECTROPHOTOMETER
- Double- beam in time – 1 photodetector
- Double-beam in space – 2 photodetectors (1- sample beam, 2- reference beam)
PARTS OF SPECTROPHOTOMETER
- LIGHT SOURCE
- Tungsten: for visible and near infrared region
- Deuterium: for UV region
- Xenon discharge lamp: for UV and Visible region
- ENTRANCE SLIT – minimizes the entry of stray light to the monochromator
- MONOCHROMATOR – isolates specific wavelength
- Prisms: light is refracted
- Diffraction gratings: light is bent; most commonly used
- Filters: light enters one side and is reflected on the other side.
- EXIT SLIT – controls bandpass (total range to which wavelengths are transmitted. The narrower the bandpass, the grater the resolution)
- CUVETTE – contains the solution (known as absorption cell/analytical cell/sample cell)
- PHOTODETECTOR – aids in the conversion of light transmitted to photoelectric energy
- Barrier layer cell: simplest. Temperature sensitive. Radiation and visible region.
- Photodiode: has excellent linearity.
- Photomultiplier tube: most commonly used. Chemiluminiscence and Fluometry. Measures visible and UV region.
- Phototube: cathode and anode enclosed in glass case. Fluometry.
- READ-OUT DEVICE – a monitor that displays the output
ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
- Measures the amount of light that have been absorbed by a ground state atom
- For measurement of unexcitable metals like calcium and magnesium
- Hollow-cathode lamp: light source
- Atomizer: used for the conversion of ions to atoms
- Chopper: used to modulate amount of light from the hollow-cathode lamp
FLAME EMISSION PHOTOMETRY
- Flame permits the excitation of the electrons; after which, electrons return to a ground state thus radiation is emitted.
- Flame serves as both light source and cuvette.
- Internal standards used: Cesium and Lithium (preferred)
- For measurement of excited ions such as sodium (yellow) and potassium (violet).
- Calcium also shows a colored (brick red) flame
FLUOROMETRY
- Light is absorbed by atoms at a specific wavelength and is emitted at a longer wavelength (with lower energy)
- Light source: xenon lamp or mercury arc
- There are two monochromators
- Primary monochromator: selects wavelength that is best absorbed by solution that is to be measured
- Secondary monochromator: this prevents the incident light from striking the detector
- Disadvantage: Quenching
TURBIDIMETRY
- Measures light blocked by molecules
- Used for immunoglobulins, immune complexes and complement
NEPHELOMETRY
- Measures light scattered by molecules
- Used for measuring amount of antigen-antibody complexes
CHROMATOGRAPHY
- Separation is based upon differences in characteristics (both physical and chemical) of substances
- Used for amino acid determination, drugs and sugars
POTENTIOMETRY
- Measures electric potential
- pH electrode – glass electrode
- pCO2 electrode
- ion – selective electrode
- Sodium: glass electrode
- Potassium: Valinomycin gel
- Chloride: Tri-N-octyl propyl ammonium chloride decanol
ELECTROPHORESIS
- Separation of proteins is aided by an electric current
| IONS | POLE |
POSITIVE | CATIONS | CATHODE |
NEGATIVE | ANIONS | ANODE |
- pH of buffer: 6
- support materials:
- Agarose gel – separation by electric charges
- Cellulose acetate – separation by molecular size
- Polyacrylamide gel – separation by charge and molecular size
ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERN OF CERTAIN CONDITIONS | |
Alpha1-globulin flat curve | Juvenile cirrhosis |
Alpha2-globulin band spike | Nephrotic syndrome |
Beta-gamma bridging | Hepatic cirrhosis |
Monoclonal gammopathy (gamma spike) | Multiple myeloma |
Polyclonal gammopathy | Rheumatoid arthritis and malignancy |
Small spike in Beta-region | Iron deficiency anemia |